The Knowledge Gap: Why You Must Use RAG, Not Training, to Solve Enterprise AI
Written By
Vishal Soni
Dec 3, 2025
16 Min Read
Stop trying to train LLMs on your data. Learn why RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is the only viable strategy for accurate, real-time Enterprise AI adoption.
TL;DR for Executives: Your LLM knows Shakespeare but nothing about your Q3 sales. Training a model on your data costs $100M+ and is obsolete by deployment. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) lets the model "read" your data in real-time without retraining - cutting costs by 99%+ while keeping information current. It's the difference between memorizing a textbook and bringing it to the exam.
You just bought an Enterprise license for the smartest LLM on the market. You type in a simple question: "How did our Q3 sales compare to the marketing budget?"
The model responds with a confident, eloquent hallucination about a company that isn't yours, or it simply apologizes: "I cannot access your private data."
This is the "Knowledge Gap." As we established in our article on how LLMs work through word prediction, the model knows how to speak English, write Python, and summarize Shakespeare, but it knows absolutely nothing about your business.
To fix this, most leaders intuitively reach for the wrong tool: Training.
The "Status Quo" Trap: The Training Fallacy
When leaders realize the model doesn't know their data, their first instinct is: "We need to train the model on our documents."
In the vast majority of cases, this is a mistake.
Training a model from scratch (or "Pre-training") involves discarding the model's existing intelligence and teaching it from the ground up. It is the "ancient" way of doing things. It is slow, statistically difficult, and astronomically expensive.
As we covered in our article on LLM training costs, GPT-4 cost over $100 million to train, and Google's Gemini 1.0 Ultra reached an estimated $192 million in 2023. Even if you have the budget, "training" fails the speed test. By the time you finish training a model on your Q3 data, Q4 is already over. The model is obsolete the moment it is deployed. [1][2][3]
The Solution: The Open-Book Test (RAG)
We don't need the model to memorize your Q3 sales data. We just need it to read the data before answering.
This is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
Think of the LLM as a brilliant student taking an exam.
Training is forcing the student to memorize the textbook.
RAG is letting the student bring the textbook into the exam room.
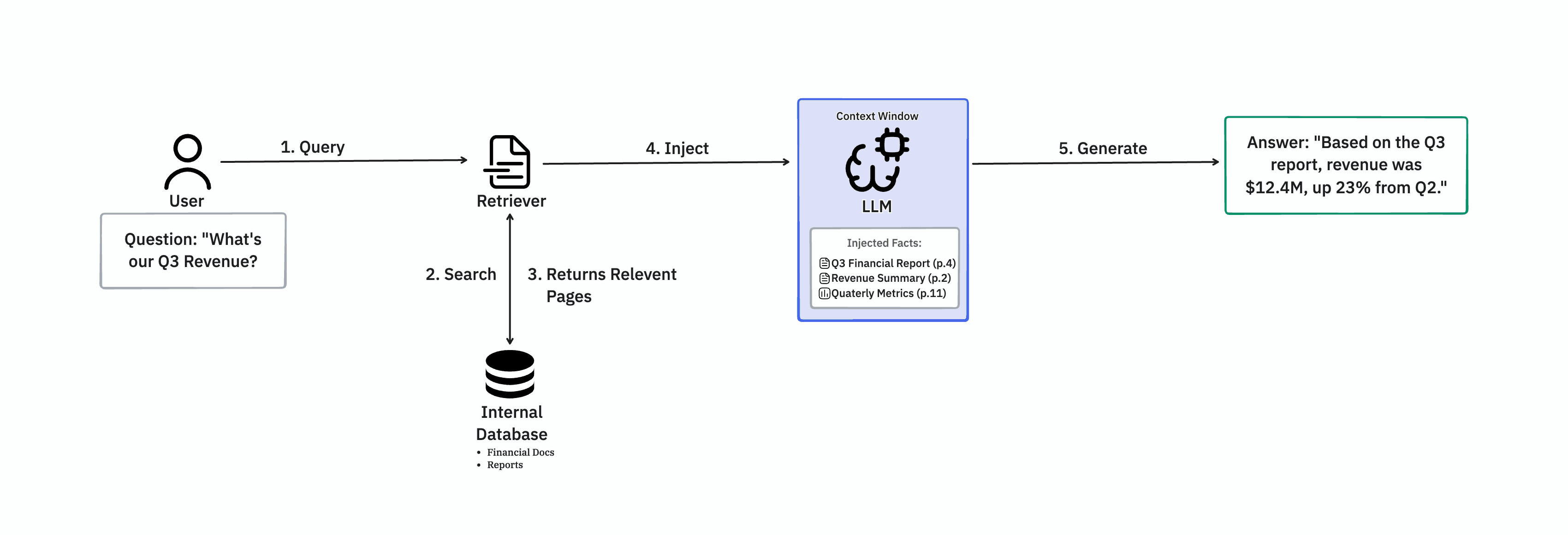
In a RAG architecture, when you ask a question, the system doesn't send it directly to the LLM. First, it searches your internal database (the "Retriever") to find the specific pages relevant to your query. It then "injects" those pages directly into the system prompt.
The LLM then uses its context window to read the facts and generate an answer. This allows you to "inject relevant facts into the application" without changing the model's weights.
The Golden Rule of AI Architecture:
RAG is for Facts (What happened in Q3?).
Fine-Tuning is for Behavior (How should we talk about it?).
The Evolution: Retrieval Engineering in 2025
Basic RAG (Retrieve-and-Generate) was the standard for 2023. However, basic RAG is brittle. It often retrieves the wrong document or misses the nuance of complex questions.
To build production-grade systems today, we use Advanced Retrieval Engineering. Here is what that looks like:
1. Agentic RAG: From Passive to Active
Traditional RAG is linear: Search → Answer. If the search fails, the answer fails.
Agentic RAG transforms the system into a problem-solver. It uses an "observe-think-act" loop. If you ask, "Compare Q3 2023 vs Q1 2024," the agent understands this requires two distinct searches. It retrieves Q3 data, analyzes it, realizes it needs Q1 data, performs a second search, and then synthesizes the answer. It validates its own work.
2. Hybrid Retrieval + Reranking
We no longer rely on a single search method. [4]
Keyword Search (BM25): Good for exact part numbers or names.
Vector Search (Semantic): Good for concepts ("Why did sales drop?").
The new standard is Hybrid Retrieval: doing both searches simultaneously and using a "Reranker" model to filter out the noise. This dual-stage approach significantly reduces irrelevant data entering the context window. When combined with reranking, contextual retrieval can reduce failed retrievals by up to 67%. [5][4]
3. Graph RAG
Standard RAG treats documents as isolated chunks of text. Graph RAG understands relationships. It maps your data into a knowledge graph (e.g., Client X is connected to Project Y which is owned by Manager Z). This allows the AI to "reason" across documents, tracing complex dependencies that a simple keyword search would miss. Microsoft Research released GraphRAG 1.0 in December 2024, marking a major milestone in production-ready graph-based retrieval. [6]
4. Contextual Retrieval
Splitting documents into small "chunks" for the AI often destroys context. If the model sees a chunk that says "Revenue was $4M," it doesn't know which company or quarter that refers to. Contextual Retrieval solves this by prepending chunk-specific explanatory context to each chunk before it is stored, ensuring the model never loses the global context. Anthropic's approach reduced top-20-chunk retrieval failure rates by 35% using Contextual Embeddings alone, and by 49% when combining Contextual Embeddings with Contextual BM25. [5]
The Business Impact
Why does this shift to RAG matter for the bottom line?
Instant Updates: You don't need to retrain or fine-tune when your pricing changes. You simply update the document in your database. The very next query will retrieve the new price.
Reduced Hallucinations: By forcing the model to cite the retrieved text, you ground the output in verified data. If the document isn't found, the system can be configured to say "I don't know" rather than making up a number.
The Hybrid Approach: The most mature organizations blend these methods. They use RAG for real-time intelligence and perform selective Fine-Tuning to ensure the model speaks in the correct corporate tone.
The 2025 playbook is not about building a bigger brain. It is about building a better library.
Key Takeaways: Implementing RAG in Your Organization
Now that you understand why RAG beats training for enterprise AI, here's how to apply this strategy:
Start with Basic RAG: Before investing in advanced techniques, implement a simple RAG system. Connect your LLM to a vector database (Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant) and test it on a single use case (e.g., internal documentation Q&A).
Audit Your Knowledge Sources: Identify which data sources need to be searchable: internal docs, customer records, product catalogs, support tickets, sales data. Prioritize based on query frequency and business impact.
Implement Hybrid Retrieval: Don't rely on vector search alone. Combine keyword search (BM25) for exact matches (part numbers, names) with semantic search for concepts. Use a reranker to filter results before sending to the LLM. [4]
Add Contextual Headers: When chunking documents, prepend each chunk with metadata (document title, section, date) so the model never loses context. "Revenue was $4M" becomes "Q3 2024 Financial Report > Revenue: Revenue was $4M." [5]
Design for Citations: Configure your RAG system to cite sources. Instead of just answering "Q3 revenue was $4M," return "Q3 revenue was $4M (Source: Q3 Financial Report, Page 3)." This reduces hallucinations and builds trust.
Monitor Retrieval Quality: Track metrics like retrieval precision (% of retrieved docs that are relevant) and recall (% of relevant docs that are retrieved). Poor retrieval quality means poor answers, regardless of LLM quality.
Combine RAG with Fine-Tuning: Use RAG for facts (what to say) and fine-tuning for behavior (how to say it). This hybrid approach delivers both accuracy and brand consistency.
The future of enterprise AI isn't about training bigger models - it's about building smarter retrieval systems that connect existing models to your proprietary data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why is "training the model" on my private data considered the "Status Quo Trap" or a "Training Fallacy"?
A: Attempting to train a general LLM on your documents is often a mistake because:
Cost and Time: Training is astronomically expensive and slow, involving discarding the model's existing intelligence and teaching it from scratch. GPT-4 cost over $100M to train, while Gemini 1.0 Ultra reached $192M. [2][3][1]
Obsolescence: By the time you finish training a model on historical data, the data is already old. The model is obsolete the moment it is deployed, failing the "speed test."
Inflexibility: Every time your data changes (new pricing, updated policies), you'd need to retrain - an impossible maintenance burden.
RAG solves all three: it's cheap (no retraining), instant (update the database, not the model), and flexible (works with any LLM).
Q2: What is the difference between basic RAG and modern "Retrieval Engineering"?
A: Basic RAG (2023 standard) is often a linear, brittle process: Search → Answer. If the search fails, the answer fails.
Modern Retrieval Engineering (2025 standard) uses advanced techniques to improve search accuracy and reasoning:
Agentic RAG: Uses an "observe-think-act" loop to break complex questions into multiple search steps, synthesizing the answer across various documents.
Hybrid Retrieval + Reranking: Combines Keyword (BM25) and Semantic (Vector) search methods, using a Reranker model to filter out irrelevant data and ensure the best results are sent to the LLM. [4]
Graph RAG: Maps data into knowledge graphs to understand relationships between entities. [6]
Contextual Retrieval: Prepends metadata to chunks so the model never loses context. [5]
Q3: How does Graph RAG help the AI reason across multiple documents?
A: Standard RAG treats documents as isolated chunks of text. Graph RAG addresses this by mapping your data into a knowledge graph that understands the relationships between entities (e.g., Client X is connected to Project Y, which is linked to Manager Z). [6]
This allows the AI to answer complex queries like "Which projects managed by Sarah are behind schedule?" by traversing the graph: Find Sarah → Find her projects → Check their status. Traditional RAG would struggle because this information is scattered across multiple documents. Microsoft's GraphRAG 1.0, released in December 2024, represents the production-ready state of this technology. [6]
Q4: Can RAG completely eliminate hallucinations?
A: No, but it dramatically reduces them. RAG grounds the model's responses in retrieved documents, but the model can still:
Misinterpret the retrieved text
Combine information from multiple sources incorrectly
Generate plausible-sounding text when retrieval fails
To minimize hallucinations:
Implement citation requirements (force the model to quote sources)
Use confidence scoring (flag low-confidence answers for human review)
Add fallback responses ("I don't have enough information" instead of guessing)
Monitor retrieval quality (ensure the right documents are being found) [5]
Q5: How does RAG compare to fine-tuning for enterprise AI?
A: They solve different problems:
RAG provides knowledge (facts, data, current information). Use it when you need the model to access proprietary or up-to-date information.
Fine-Tuning provides behavior (tone, format, style). Use it when you need the model to respond in a specific way or follow strict output formats.
Best Practice: Use both. RAG gives the model access to your data, fine-tuning teaches it how to present that data in your brand voice. This combination delivers both accuracy and consistency.
Citations
Wikipedia - GPT-4 (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPT-4)
Focus on Business - Gemini Ultra Training Costs (https://focusonbusiness.eu/en/news/gemini-ultra-training-costs-in-2023-neared-200-million-more-than-2x-gpt4/6170)
Visual Capitalist - The Surging Cost of Training AI Models (https://www.visualcapitalist.com/the-surging-cost-of-training-ai-models/)
Superlinked - Optimizing RAG with Hybrid Search & Reranking (https://superlinked.com/vectorhub/articles/optimizing-rag-with-hybrid-search-reranking)
Instructor - Implementing Anthropic's Contextual Retrieval (https://python.useinstructor.com/blog/2024/09/26/implementing-anthropics-contextual-retrieval-with-async-processing/)
Microsoft Research - GraphRAG: Unlocking LLM discovery on narrative private data (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-unlocking-llm-discovery-on-narrative-private-data/)